Licorice
Licorice Detailed Encyclopedia
Licorice is a commonly used tonic Chinese herbal plant, known as the 'Elder Statesman of Herbs', with effects of tonifying spleen and qi, clearing heat and detoxifying, expelling phlegm and relieving cough, moderating and relieving pain, and harmonizing other herbs. Mainly distributed in Xinjiang, Gansu, and Inner Mongolia of China, it is one of the most widely used herbs in traditional Chinese herbal practice.
Basic Information
Family:Fabaceae
Scientific Name:Glycyrrhiza uralensis
Origin:Xinjiang, Gansu, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia of China
Harvest Period:Autumn (September-October)
Growth Years:3-4 years
Plant Height:40-100 cm
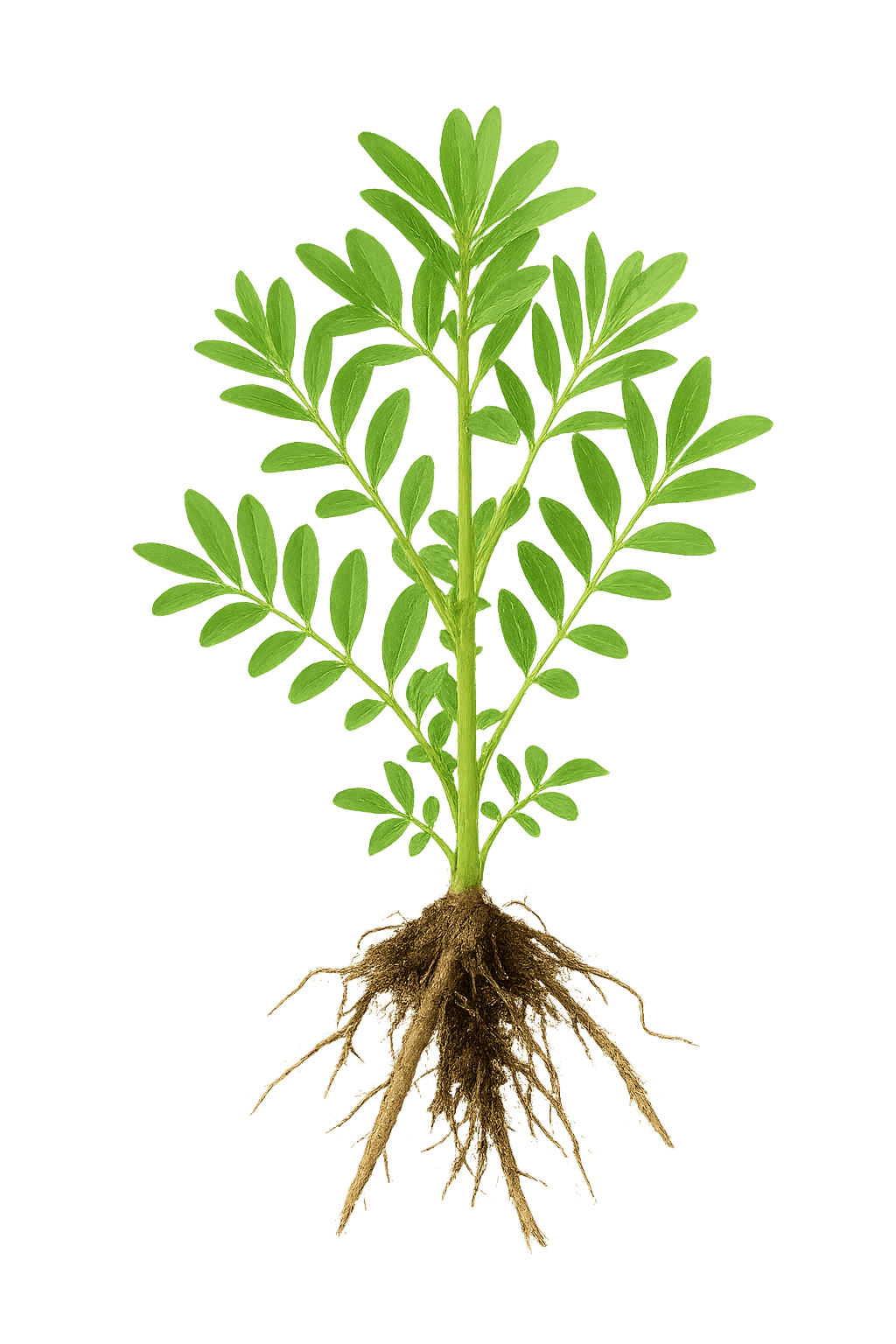
Morphological Characteristics
Leaves:Odd-pinnate compound leaves with 7-17 leaflets, ovate or broadly ovate
Flowers:Raceme inflorescence, purple or pale purple flowers, blooming June-July
Roots:Thick cylindrical taproot, reddish-brown outer skin, yellow cross-section, sweet taste
Stem:Erect, covered with glandular scales and spines
Growth Environment
Soil Requirements:Sandy loam with good drainage, pH 7.5-8.5
Water Requirements:Drought-tolerant, avoid waterlogging, moderate watering
Light Requirements:Sun-loving, requires full sunlight
Temperature Requirements:15-25°C, strong cold and heat tolerance
Humidity Requirements:Relative humidity 40-60%, drought-tolerant
Classification & Varieties
Main Varieties
Processing Types
💊 Health Benefits
Nature & Taste:Sweet, neutral
Meridian:Enters Heart, Lung, Spleen, Stomach meridians
Main Efficacies
- •Tonifies spleen and qi, suitable for spleen-stomach weakness, fatigue, palpitations and shortness of breath
- •Clears heat and detoxifies, treats sore throat, carbuncles and sores
- •Expels phlegm and relieves cough, improves cough with phlegm, asthma
- •Moderates and relieves pain, relieves abdominal pain, limb spasms
- •Harmonizes other herbs, enhances efficacy and reduces toxicity of other medicines
Active Ingredients
📖 Usage Methods
Dosage
- •Decoction: 2-10g
- •Powder: 1-3g
- •Stew: Add to herbal formulas to harmonize
- •Tea: Slice and steep in water
⚠️ Contraindications
- •Use with caution in dampness obstruction and fullness, vomiting
- •Long-term large doses may cause edema and hypertension
- •Pregnant women use in moderation
- •Children use in moderation
🌱 Cultivation Techniques
Cultivation Points
- •Select sunny location with deep soil layer
- •Deep tillage, apply organic fertilizer
- •Spring sowing, row spacing 40-50cm
- •Timely weeding, moderate watering and fertilizing
Common Pests & Diseases
Prevention Measures:Strengthen field management, rational crop rotation
Treatment Methods:Spray carbendazim or bordeaux mixture at early stage
✂️ Harvest & Processing
Harvest Timing:Autumn September-October, harvest after 3-4 years of growth
Harvest Method:Dig up roots, remove stems and fibrous roots
Processing Methods
- •Raw licorice: Wash, slice and sun-dry
- •Honey-fried licorice: Honey-fried to enhance qi-tonifying effect
- •Roasted licorice: Roasted to enhance spleen-tonifying effect
Storage:Store in cool, dry place, prevent moisture and insects
🏛️ Cultural Value
History:Licorice has been used for over 3000 years, listed as superior grade in Shennong's Classic of Materia Medica
Symbolism:Symbolizes harmony and moderation
Gift Culture:Traditional harmonizing herb in formulas
Modern Research:Modern research confirms anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and liver-protecting effects
Market Value:Xinjiang licorice is of excellent quality, an important herbal material and export commodity