Azalea
Azalea Detailed Encyclopedia Introduction
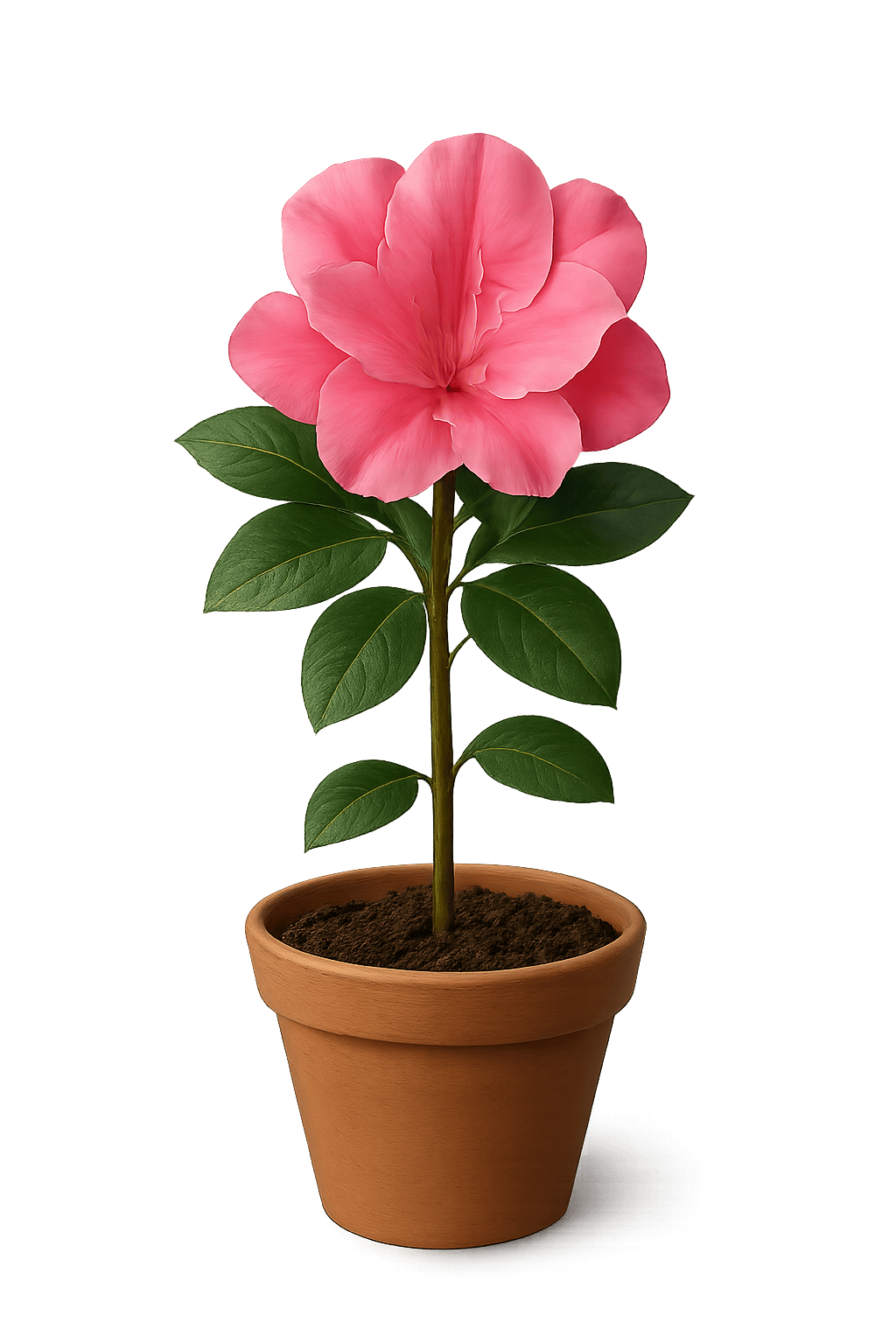
Evergreen or deciduous shrub with vibrant spring blooms, popular in gardens and container displays.
Basic Info
Family:Ericaceae
Scientific Name:Rhododendron
Origin:Asia, North America
Flowering Period:Spring to early summer
Height:0.3-4 meters
Lifespan:Perennial
Morphology
Leaves:Elliptical or obovate, leathery or papery texture
Flowers:Funnel-shaped or bell-shaped, rich in colors
Roots:Shallow root system with well-developed fibrous roots
Stem:Multi-branched, woody
Growth Habits
Soil Requirements:Acidic, well-drained humus-rich soil
Watering Needs:Keep soil moist, avoid waterlogging
Light Requirements:Partial shade to filtered light
Temperature Requirements:15-25°C, cold hardiness varies by variety
Classification & Varieties
Main Classifications
Ornamental Varieties
Professional Care
✂️ Pruning Management
Pruning Timing:After flowering, autumn shaping
Pruning Method:Light pruning, remove weak and diseased branches
Pruning Purpose:Maintain plant shape, promote flowering
Required Tools:Pruning shears, disinfectant
🛡️ Pest & Disease Management
Common Pests:
Common Diseases:
Prevention Measures:Maintain ventilation, avoid excessive moisture, regular inspection
Treatment Methods:Biological control, chemical agents, physical control
🌱 Fertilization Management
Fertilizer Type:Acidic fertilizer, organic fertilizer, compound fertilizer
Fertilization Frequency:Once a month during growing season
Fertilization Timing:Spring budding period, after flowering, autumn
Fertilization Amount:20-50 grams per plant depending on size
💧 Water Requirements
Watering Frequency:Every 2-3 days in spring/summer, weekly in autumn/winter
Watering Amount:Water thoroughly but avoid waterlogging, keep soil moist
Watering Method:Water at root zone, avoid water on foliage
Dehydration Signs:Wilted leaves, dry soil, stunted new growth
Basic Care Tips
- •Choose acidic soil with pH between 4.5-6.0
- •Keep soil moist but not waterlogged during spring flowering
- •Provide shade in summer, avoid direct strong sunlight
- •Prune spent flowers promptly to encourage new growth
- •Protect from cold in winter, outdoor plants need mulching
Ecology Value
Pollinators:Bees, butterflies, moths
Wildlife:Provides nectar for insects, habitat for birds
Environmental Value:Beautifies surroundings, purifies air
Cultural Symbolism
Symbolic Meaning:Prosperity, beauty, homesickness, resilience
Historical Background:Traditional Chinese flower with over a thousand years of cultivation history
Related Festivals:Azalea Festival, Spring Flower Shows
Artistic Expression:Common subject in poetry and literature